Hurricane Tracks: Cumulative - 1950 - 2020
Details
Permalink to Details- Added to the Catalog
- Available for
- SOS
- Explorer
- Categories
- Air: Tropical Cyclones, Weather
- Water: Tropical Cyclones
- Keywords
- Atmosphere
- Hurricane Tracks
- Hurricanes
- Severe Weather
- Tracks
- Tropical Cyclones
Description
Permalink to DescriptionTracking historical hurricanes is an important way for hurricane researchers to learn about the paths of future hurricanes. Because of this, records of hurricane paths are archived and studied. Not all hurricanes follow the same path, but there are certainly noticeable trends for hurricane paths. Many computer models that have been created to predict hurricane paths include the historical data in their models.
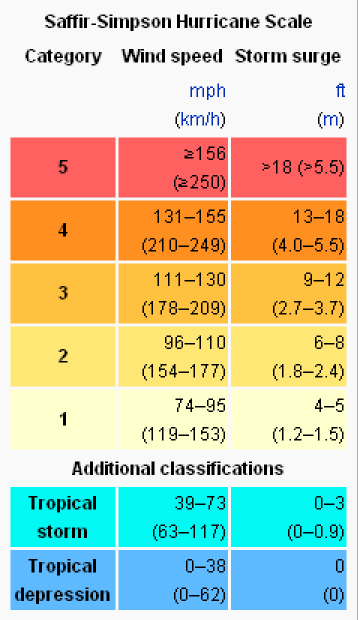
This dataset shows the paths of all tropical cyclones from 1950 through 2020. Each line is a tropical cyclone, whether a tropical depression or tropical storm (blue, cyan) or hurricane (yellow to red). The maximum sustained wind speed, with cool colors for slower speeds and warm colors for faster speeds, are indicated by the colorbar. When mapped like this, definite patterns in cyclone paths are clear to see. For example, you can see that cyclones typically start near the equator and move away from it toward the poles and they don't cross the equator.
Want to learn about a specific hurricane that affected you or someone you know? Check out this Historical Hurricanes site.
Paper Globe Cutouts are available for this dataset!
Next Generation Science Standards
Permalink to Next Generation Science StandardsCross-cutting Concepts
Permalink to Cross-cutting ConceptsGrades 3–5
C3 Scale Proportion and Quantity. Students recognize natural objects and observable phenomena exist from the very small to the immensely large. They use standard units to measure and describe physical quantities such as weight, time, temperature, and volume.
C7 Stability and Change. Students measure change in terms of differences over time, and observe that change may occur at different rates. Students learn some systems appear stable, but over long periods of time they will eventually change.
Grades 6–8
C1 Patterns. Students recognize that macroscopic patterns are related to the nature of microscopic and atomic-level structure. They identify patterns in rates of change and other numerical relationships that provide information about natural and human designed systems. They use patterns to identify cause and effect relationships, and use graphs and charts to identify patterns in data.
C3 Scale Proportion and Quantity. Students observe time, space, and energy phenomena at various scales using models to study systems that are too large or too small. They understand phenomena observed at one scale may not be observable at another scale, and the function of natural and designed systems may change with scale. They use proportional relationships (e.g., speed as the ratio of distance traveled to time taken) to gather information about the magnitude of properties and processes. They represent scientific relationships through the use of algebraic expressions and equations
C4 Systems and System Models. Students can understand that systems may interact with other systems; they may have sub-systems and be a part of larger complex systems. They can use models to represent systems and their interactions—such as inputs, processes and outputs—and energy, matter, and information flows within systems. They can also learn that models are limited in that they only represent certain aspects of the system under study.
C7 Stability and Change. Students explain stability and change in natural or designed systems by examining changes over time, and considering forces at different scales, including the atomic scale. Students learn changes in one part of a system might cause large changes in another part, systems in dynamic equilibrium are stable due to a balance of feedback mechanisms, and stability might be disturbed by either sudden events or gradual changes that accumulate over time
Grades 9–12
C3 Scale Proportion and Quantity. Students understand the significance of a phenomenon is dependent on the scale, proportion, and quantity at which it occurs. They recognize patterns observable at one scale may not be observable or exist at other scales, and some systems can only be studied indirectly as they are too small, too large, too fast, or too slow to observe directly. Students use orders of magnitude to understand how a model at one scale relates to a model at another scale. They use algebraic thinking to examine scientific data and predict the effect of a change in one variable on another (e.g., linear growth vs. exponential growth).
C4 Systems and System Models. Students can investigate or analyze a system by defining its boundaries and initial conditions, as well as its inputs and outputs. They can use models (e.g., physical, mathematical, computer models) to simulate the flow of energy, matter, and interactions within and between systems at different scales. They can also use models and simulations to predict the behavior of a system, and recognize that these predictions have limited precision and reliability due to the assumptions and approximations inherent in the models. They can also design systems to do specific tasks.
C7 Stability and Change. Students understand much of science deals with constructing explanations of how things change and how they remain stable. They quantify and model changes in systems over very short or very long periods of time. They see some changes are irreversible, and negative feedback can stabilize a system, while positive feedback can destabilize it. They recognize systems can be designed for greater or lesser stability
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Permalink to Disciplinary Core IdeasGrades 3–5
ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems. Four major Earth systems interact. Rainfall helps to shape the land and affects the types of living things found in a region. Water, ice, wind, organisms, and gravity break rocks, soils, and sediments into smaller pieces and move them around
ESS2.C The Roles of Water in Earth's Processes. Most of Earth’s water is in the ocean and much of the Earth’s fresh water is in glaciers or underground.
ESS2.D Weather & Climate. Climate describes patterns of typical weather conditions over different scales and variations. Historical weather patterns can be analyzed so that they can make predictions about what kind of weather might happen next.
ESS3.B Natural Hazards. A variety of hazards result from natural processes; humans cannot eliminate hazards but can reduce their impacts.
ESS3.C Human Impact on Earth systems. Societal activities have had major effects on the land, ocean, atmosphere, and even outer space. Societal activities can also help protect Earth’s resources and environments.
ESS3.D Global Climate Change. If Earth’s global mean temperature continues to rise, the lives of humans and other organisms will be affected in many different ways.
PS4.C Information Technologies and Instrumentation. Patterns can encode, send, receive and decode information.
Grades 6–8
ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems. Energy flows and matter cycles within and among Earth’s systems, including the sun and Earth’s interior as primary energy sources. Plate tectonics is one result of these processes.
ESS2.C The Roles of Water in Earth's Processes. Water cycles among land, ocean, and atmosphere, and is propelled by sunlight and gravity. Density variations of sea water drive interconnected ocean currents. Water movement causes weathering and erosion, changing landscape features.
ESS2.D Weather & Climate. Complex interactions determine local weather patterns and influence climate, including the role of the ocean.
ESS3.B Natural Hazards. Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region and understanding related geological forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and severe weather.
ESS3.C Human Impact on Earth systems. Human activities have altered the biosphere, sometimes damaging it, although changes to environments can have different impacts for different living things. Activities and technologies can be engineered to reduce people’s impacts on Earth.
ESS3.D Global Climate Change. Human activities affect global warming. Decisions to reduce the impact of global warming depend on understanding climate science, engineering capabilities, and social dynamics.
PS4.C Information Technologies and Instrumentation. Waves can be used to transmit digital information. Digitized information is comprised of a pattern of 1s and 0s.
Grades 9–12
ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems. Feedback effects exist within and among Earth’s systems.The geological record shows that changes to global and regional climate can be caused by interactions among changes in the sun’s energy output or Earth’s orbit, tectonic events, ocean circulation, volcanic activity, glaciers, vegetation, and human activities.
ESS2.C The Roles of Water in Earth's Processes. The planet’s dynamics are greatly influenced by water’s unique chemical and physical properties.
ESS2.D Weather & Climate. The role of radiation from the sun and its interactions with the atmosphere, ocean, and land are the foundation for the global climate system. Global climate models are used to predict future changes, including changes influenced by human behavior and natural factors
ESS3.B Natural Hazards. Natural hazards and other geological events have shaped the course of human history at local, regional, and global scales. Human activities can contribute to the frequency and intensity of some natural hazards.
ESS3.C Human Impact on Earth systems. Sustainability of human societies and the biodiversity that supports them requires responsible management of natural resources, including the development of technologies that produce less pollution and waste and that preclude ecosystem degradation.
ESS3.D Global Climate Change. Global climate models used to predict changes continue to be improved, although discoveries about the global climate system are ongoing and continually needed.
PS4.C Information Technologies and Instrumentation. Large amounts of information can be stored and shipped around as a result of being digitized.
Notable Features
Permalink to Notable Features- All recorded hurricanes worldwide from 1950 - 2020 are included
- No hurricanes cross the equator
- Very few hurricanes make it to South America because of wind shear patterns.
Data Source
Permalink to Data SourceInternational Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship, NOAA NCEI - IBTrACS version 4